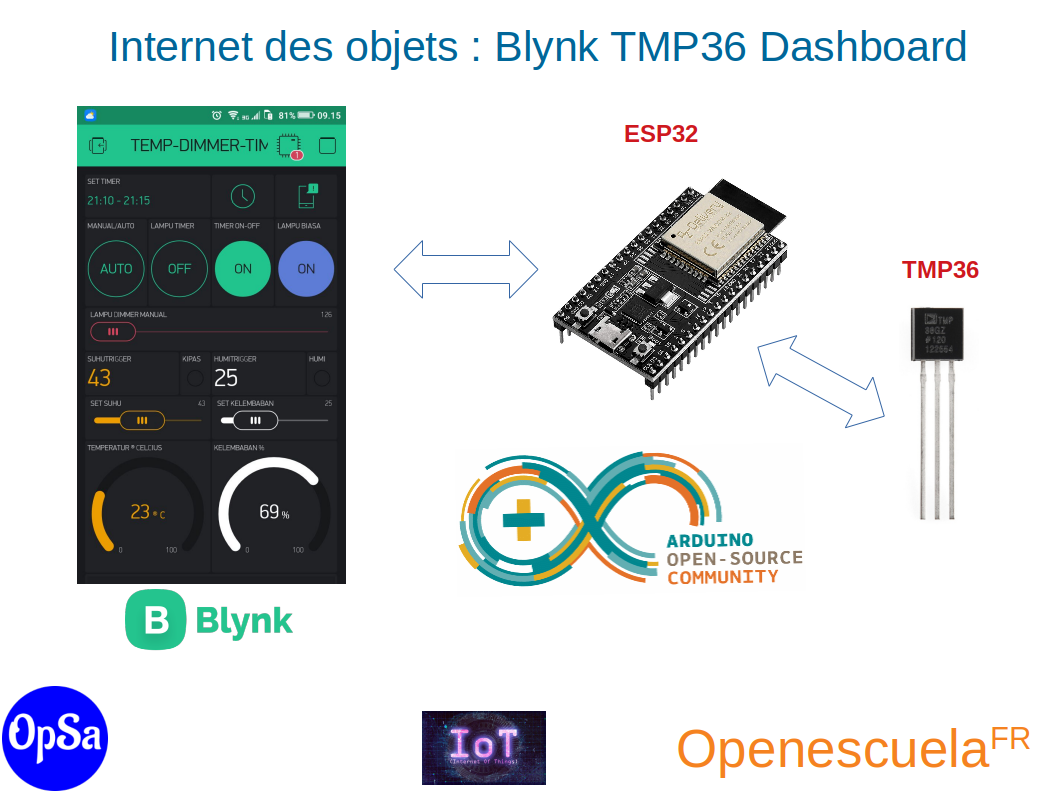
In this training, you will learn the basics of the Internet of Things. In this part, you will learn how to visualize on an IoT platform (Blynk) the data acquired from a TMP36 temperature sensor.
Temperature data acquisition program from the TMP36 using the ESP32 card:
int sensorPin = 34;
float pinVal = 0;
float voltVal = 0;
float tempVal = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
pinVal = analogRead(sensorPin);
voltVal = pinVal / 1024;
tempVal = (voltVal - 0.5) * 100;
Serial.print(tempVal); Serial.println("°C");
delay(500);
}
Program to send temperature data to the dashboard:
/* Comment this out to disable prints and save space */
#define BLYNK_PRINT Serial
/* Fill-in your Template ID (only if using Blynk.Cloud) */
//#define BLYNK_TEMPLATE_ID "YourTemplateID"
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <WiFiClient.h>
#include <BlynkSimpleEsp32.h>
// You should get Auth Token in the Blynk App.
// Go to the Project Settings (nut icon).
char auth[] = "743wLRFWj7tZz5o1VPyaoDmg42HQFx2c";
// Your WiFi credentials.
// Set password to "" for open networks.
char ssid[] = "opsa";
char pass[] = "op+sa=opsa";
int sensorPin = 34;
float pinVal = 0;
float voltVal = 0;
float tempVal = 0;
BlynkTimer timer;
void sendTemp()
{
pinVal = analogRead(sensorPin);
voltVal = pinVal / 1024;
tempVal = (voltVal - 0.5) * 100;
Serial.print(tempVal); Serial.println("°C");
Blynk.virtualWrite(V3, tempVal);
}
void setup()
{
// Debug console
Serial.begin(9600);
Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass);
timer.setInterval(1000L, sendTemp);
}
void loop()
{
Blynk.run();
timer.run();
}






0 comment